microcirculation diagnosis microscope what it and why?
What microcirculation diagnosis microscope?
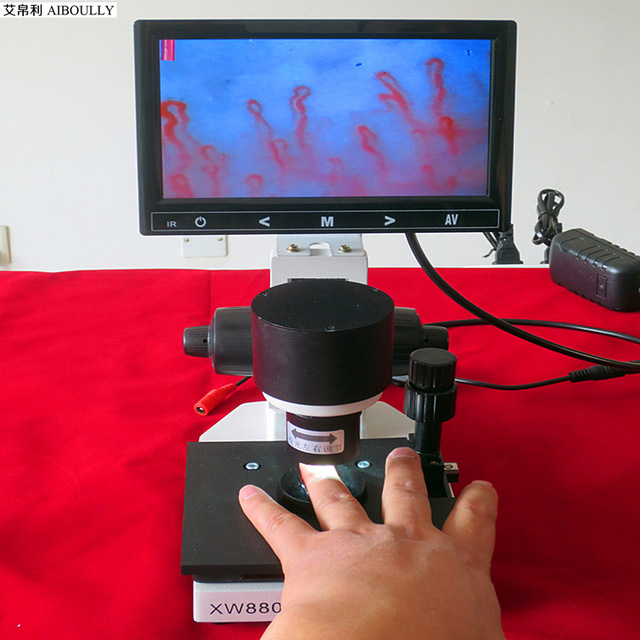
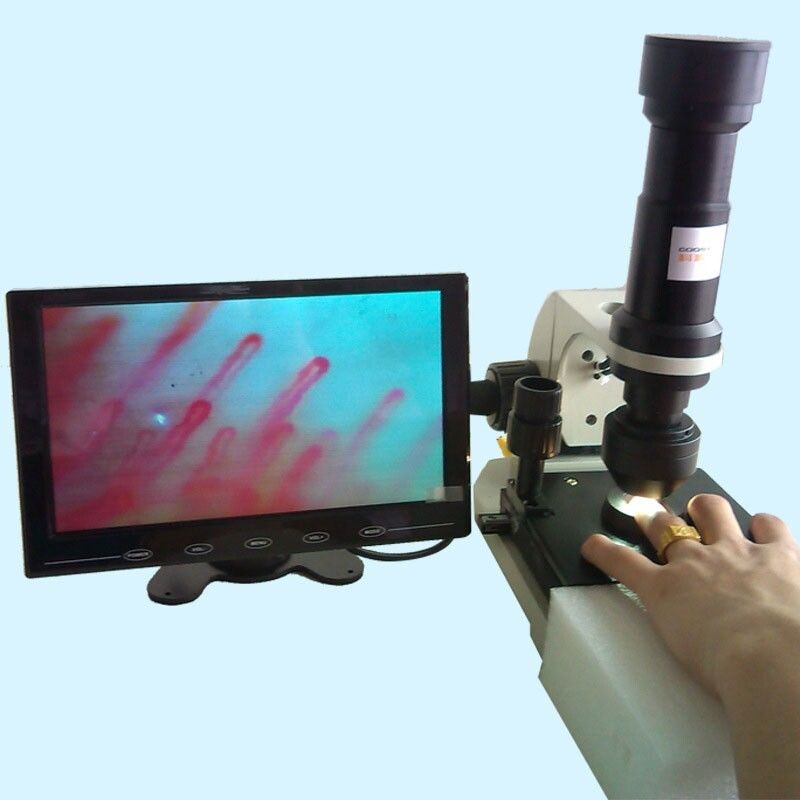
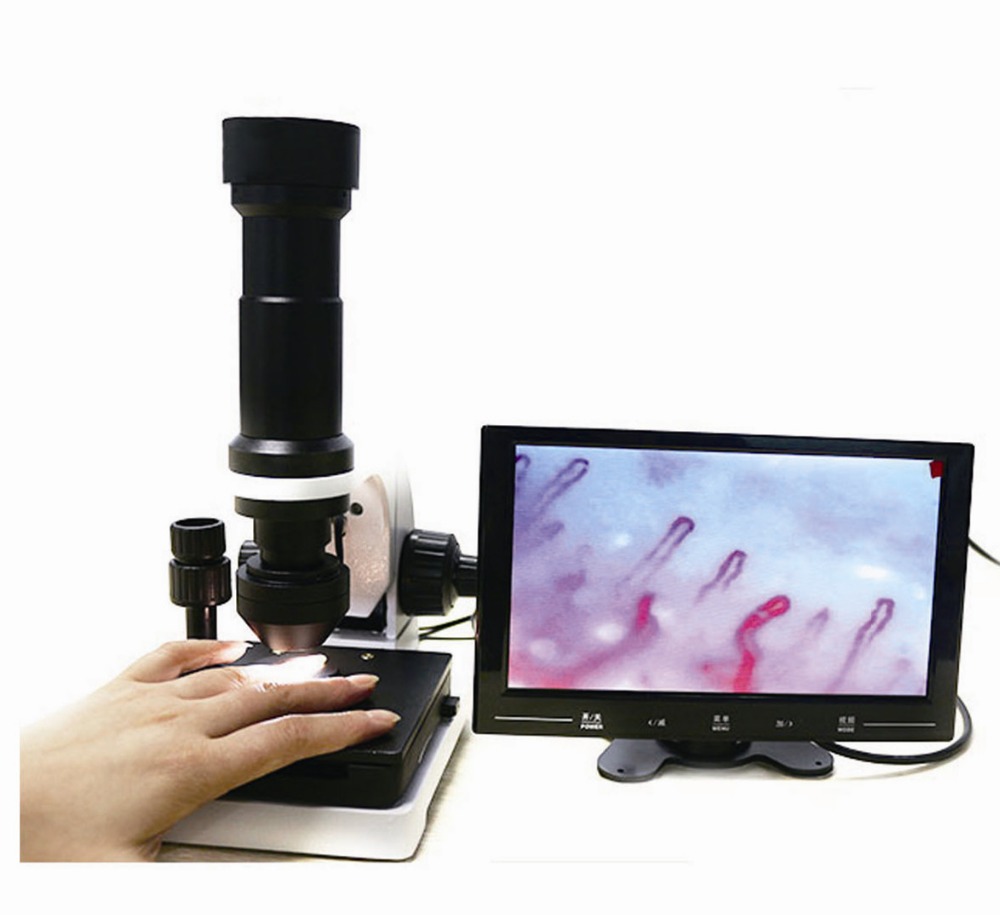

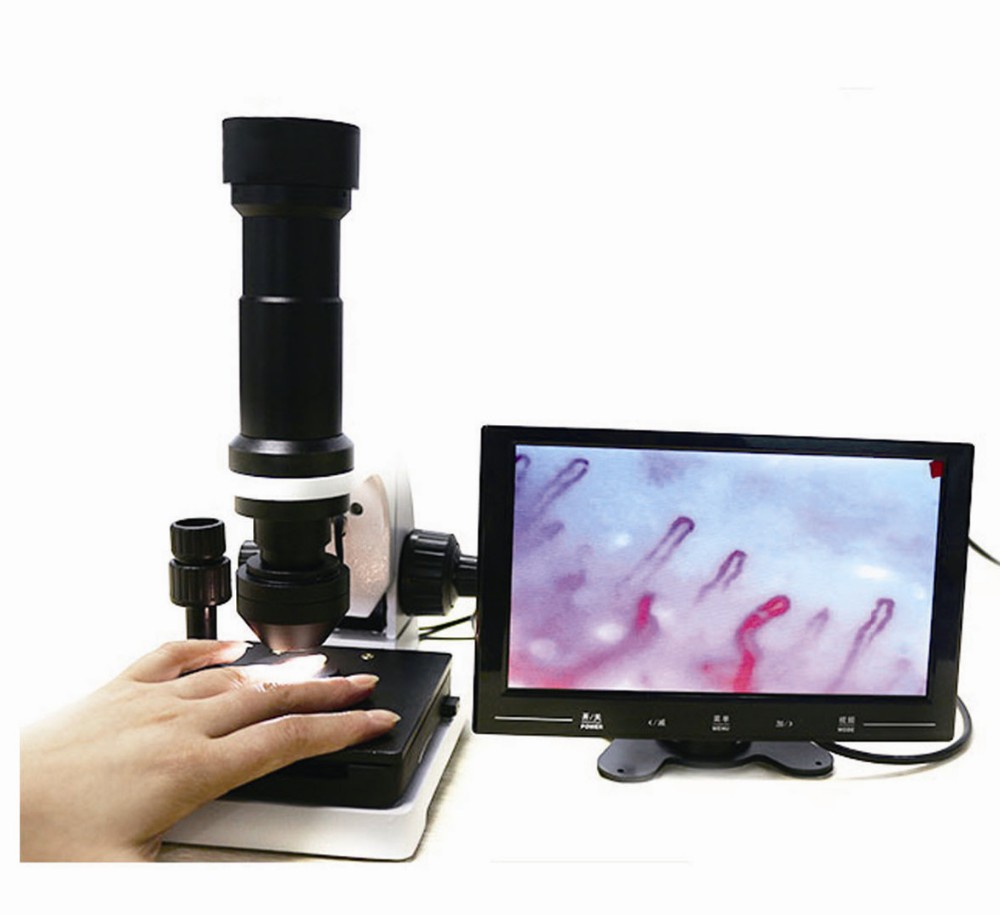

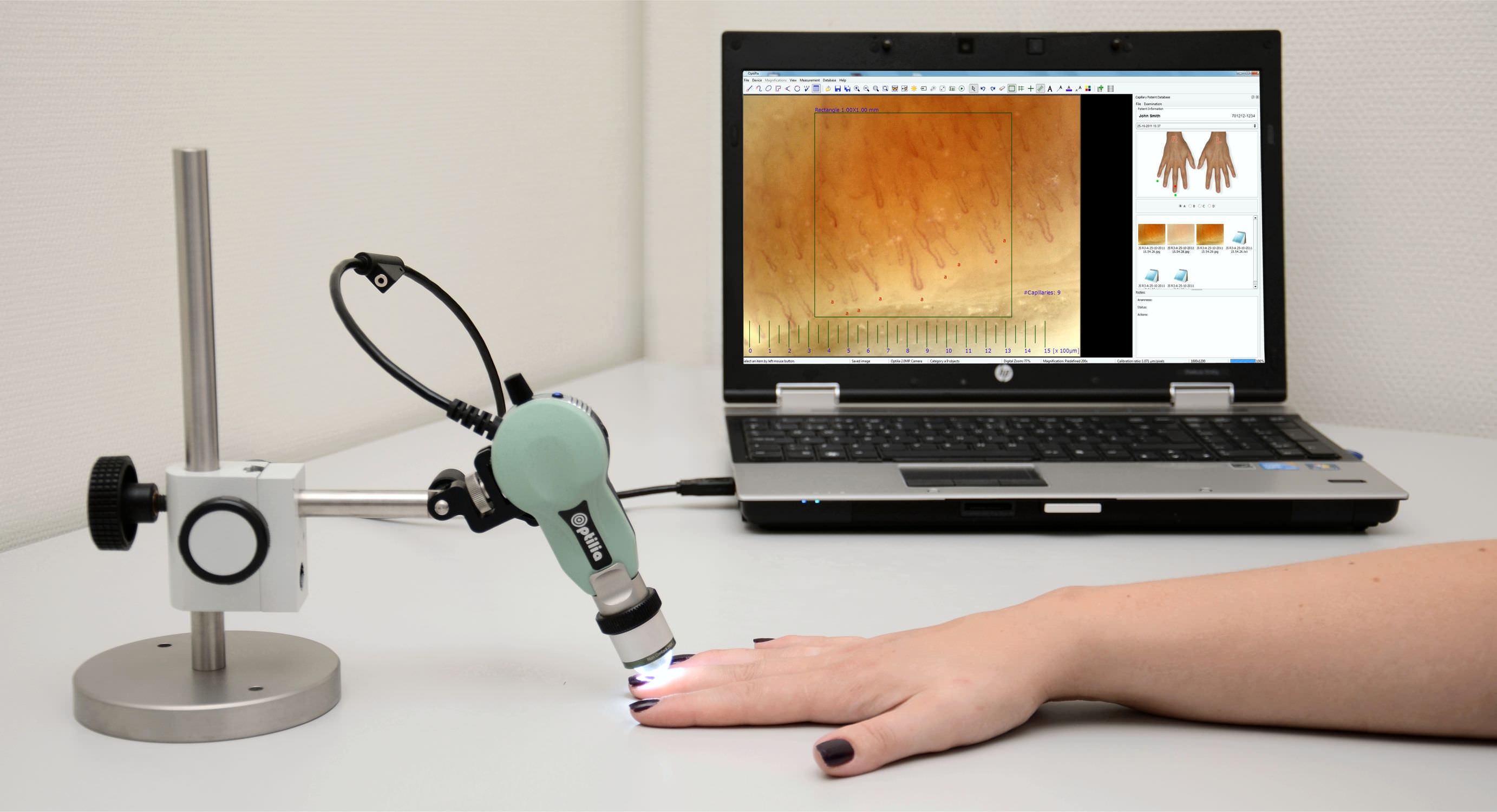
an intravitam method of study involving the examination, under magnification, of capillaries of the epithelial or endothelial integuments of animals and man (skin, mucous membranes).In man, the capillaries are examined in the skin fold of the nail bed, where they can be viewed most conveniently. A microscope or a special instrument, the capillaroscope, is used for this purpose. The use of the microscope (20–100 power magnification) after the application of a drop of clarifying oil to the skin and good oblique illumination provide good visibility. Changes are observed in the capillaries with disturbances of the peripheral blood circulation of a variety of etiologies (in vascular neuroses, the early stages of cardiac insufficiency, end arteritis obliterans). The changes observed during capillaroscopy are not strictly specific to a given pathological condition; they arise as an adaptive mechanism to any disturbance of the general blood flow. There-fore, capillaroscopy is used only as a supplementary diagnostic method in general clinical examinations.
what can do by microcirculation diagnosis microscope?
Clinical capillaroscopy for Raynaud phenomenon, rheumatic diseases.Nailfold capillaroscope,Our Nailfold Capillaroscope is the First Brand in China,Our Customers are all over the world,Capillaroscopy is a widely used technique for the examination of patients suffering from rheumatic and cardiovascular diseases, endocrine disorders, metabolic diseases, some diseases of respiratory organs,inflammatory processes and trophic disturbances and pathologies of the skin and of the hypoderm.Videocapillaroscopy is also a reliable tool in the diagnosis of angiopathies in patients suffering from pancreatic diabetes.
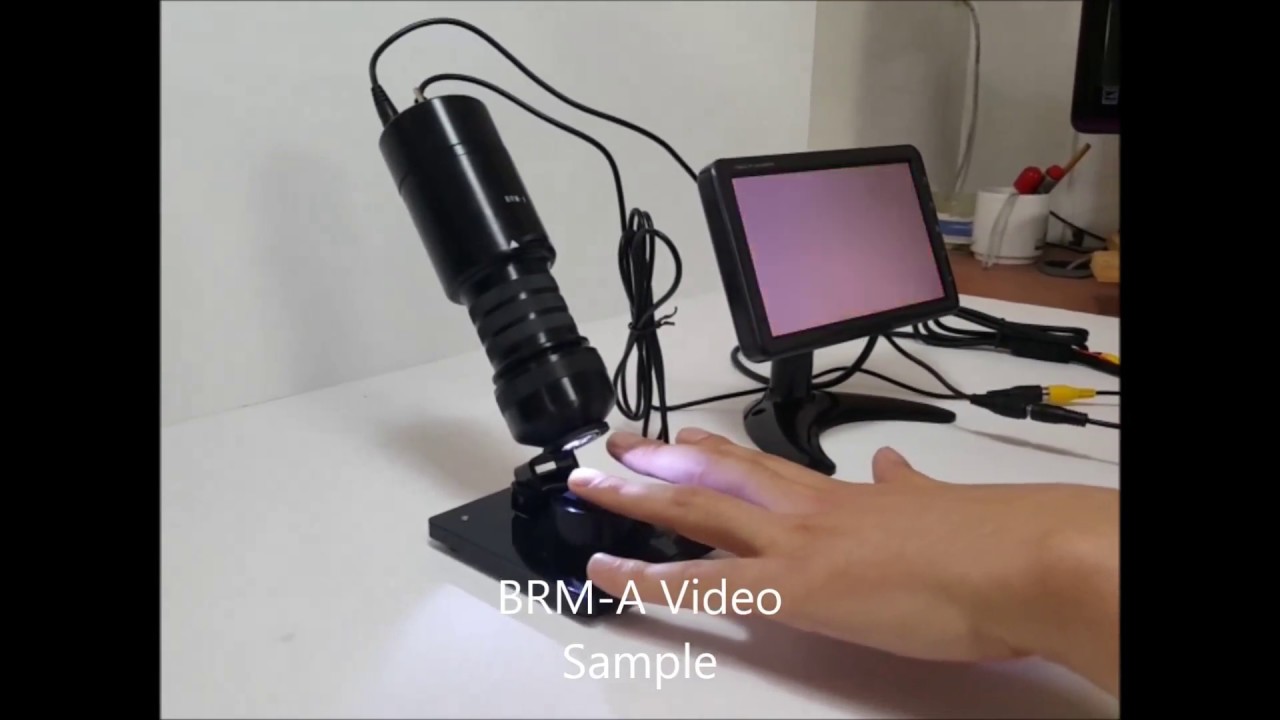
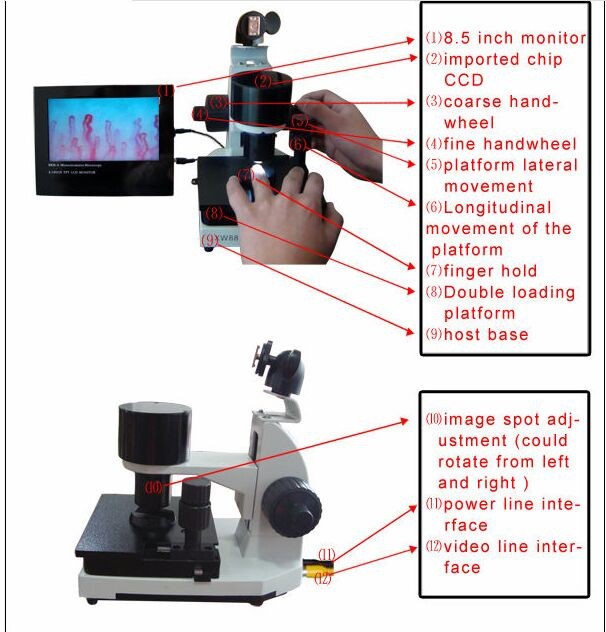


microcirculation diagnosis microscope finds application in the fields of:
Rheumatology (autoimmune diseases, Raynaud’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, sclerodermia related pathologies, systemic lupus erythematosus).
Dermatology(naevi, dermatitis, dermatosis, psoriasis, skin cancer and amartomes, non healing wounds).
Vascular Surgery (varicose veins of lower extremities, arterial spiders, cellulitis, obliterating endarteritis, skin ulces).
Angiology and Flebology (ischaemic heart disease, hypertension, pneumatic hammer disease, skin ulcers).
Aesthetic medicine and surgery (skin check-up, “aging skin”, assessment of fat tissues vasularization, liposuction, collagene injection, cellulitis,
monitoring of laser treatment effects, electrolipolysis, ultrasound, adipoclasy)
The possibility of detectiong early stages (symptomless) of vessel disorders by videocapillaroscopy opens up new possibilities for the prophylaxis of several diseases.Nailfold Video Capillaroscope -Top selling model
why microcirculation diagnosis microscope?
What is microcirculation diagnosis microscope?
The capillaroscopy is a non-invasive technique at nailfold level, making it possible to assess the characteristics of the nailfold distal capillaries, thanks to a lens and a light that shines on said spot.
The information it provides us with helps to complete the diagnosis of the vasculitic autoimmune process of the patient; it does not permit a diagnosis or specific therapeutic approach on its own.
For its correct visualisation, the patient is recommended:
Not to wear nail varnish and to avoid external harm (bumps, wounds, nail biting)
Not to smoke in the 2 hours prior to the test
To remain in the a room with a temperature of between 22ºC and 25ºC to avoid vasoconstriction episodes due to exogenous factors.
WHAT ARE microcirculation diagnosis microscope USES?
The capillaroscopy allows us to know the extent of the distal vascularisation, which is very important in systemic sclerosis and other connective pathologies, as well as to rule out systemic involvement in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon with no other associated clinical involvement.
RAYNAUD IS PHENOMENON
The capillaroscopy of the nail bed is a simple, bloodless, economical method which is very useful for studying Raynaud’s phenomenon and other rheumatological conditions. Raynaud’s phenomenon can be defined as the change in the colouring of the fingers and/or toes in response to cold or stress. It traditionally progresses through three stages: paleness (vasospasm), cyanosis (due to increased carboxyhemoglobin) and erythema (reactive hiperemia).
Raynaud’s phenomenon can be primary (Raynaud’s disease) or secondary, associated with a connective tissue disease. Primary Raynaud’s phenomenon is responsible for around 60% of all new cases. 15-20% of cases of Raynaud’s phenomenon are due to a series of non- immunological processes, such as drugs, occupational diseases, neoplasms, etc. The remaining 15-20% are associated with connective tissue diseases.
Raynaud’s is present in over 90% of patients with scleroderma and in 70% of cases it is the first symptom. Although it seems impossible to predict that a patient with Raynaud’s will develop scleroderma, the presence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) indicates a greater risk of onset.

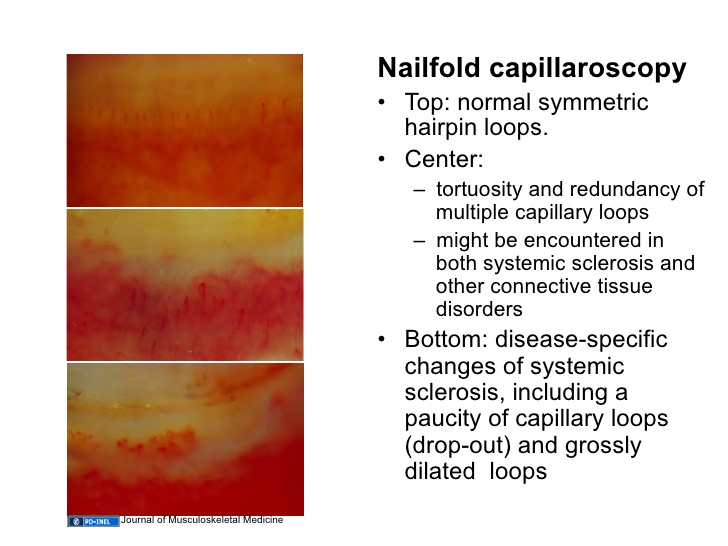
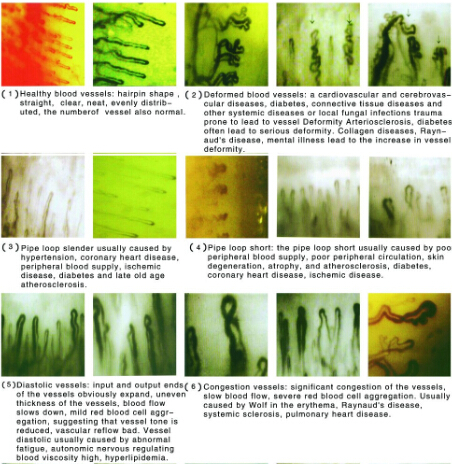
SCLERODERMA
The nail bed capillaroscopy shows morphological alterations at an early stage in some connective tissue diseases of maximum rheumatological interest, particularly capillaroscopy. In these cases, the capillaroscopy traditionally shows the “sclerodermic pattern” characterised by: reduction or absence of capillaries in patches, capillary dilation, and sometimes mega-capillaries and splinter haemorrhages. This “sclerodermic pattern” appears early and when it is observed in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon, even if it is not very obvious, it should lead to the search for sclerodermic manifestations in internal organs, which can be present without causing any symptoms. The combination of Raynaud’s phenomenon and a “sclerodermic pattern” in a capillaroscopy can precede and therefore predict the onset of scleroderma.
microcirculation microscope price
microcirculation microscope malaysia
microcirculation diagnosis microscope
nailfold microcirculation microscope
video microscopy microcirculation
microcirculation microscope
microcirculation diagnosis microscope AND RHEUMATOLOGICAL CONDITIONS
In dermatomyositis, the capillaroscopy is similar and sometimes indistinguishable from that found in scleroderma. These patients generally present the other clinical, enzymatic or electromyographic manifestations of dermatomyositis that enable its recognition and diagnosis.
In mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) or overlap syndromes that a sclerodermic component, the findings of the capillaroscopy can be similar although rarely are large capillary dilations and mega-capillaries observed. These capillaroscopies must be analysed by an expert.
In systemic lupus erythematosus, the alterations in the capillaroscopy are non-specific, and it is possible to find focal capillary reduction, albeit not very strong. The capillaries can be somewhat dilated and tortuous, sometimes with criss-crossing of the arterial and venous components (ringlets), the latter being the most characteristic finding in the capillaroscopy.
In primary Raynaud’s phenomenon, the most striking characteristic is the elongated capillaries with undulations throughout the arterial and venous components. Little or no reduction or dilation of the capillaries can be observed. Splinter haemorrhages are scarce and small.
Ultimately, this is an auxiliary diagnostic technique with great value in rheumatology and vascular disease.
What is microcirculation diagnosis microscope?
nailfold capillary microscopy Widefield capillary microscopy A technique used to evaluate finger nailfold capillaries, using a wide-angle stereomicroscope or ophthalmoscope; enlargement, ↑ tortuosity, or ↓ number of capillaries occur in connective tissue diseases–eg, Raynaud’s phenomenon, scleroderma–to evaluate extent of visceral involvement, MCTD, dermatomyositis, SLE.
Abstract. Nailfold capillaroscopy is a method of great diagnostic value in the differential diagnosis of primary versus secondary Raynaud´s phenomenon, of systemic sclerosis versus other so called connective tissue diseases and of additional diagnostic value in other entities. Rheumatologists, dermatologists, and angiologists in Germany have convened in an interdisciplinary working group in which they synergistically combined their expertise to develop a common nomenclature and standards for the technical performance of nailfold capillary microscopy. The article gives an overview of historical and technical aspects of capillaroscopy, morphologic findings, and disease-specific patterns. It also provides a critical appraisal of its significance in the diagnosis and sequelae of these interdisciplinarily-managed diseases including its performance in children and gives an excursion in the potential perspectives of capillaroscopy in less common indications.
Related Items













